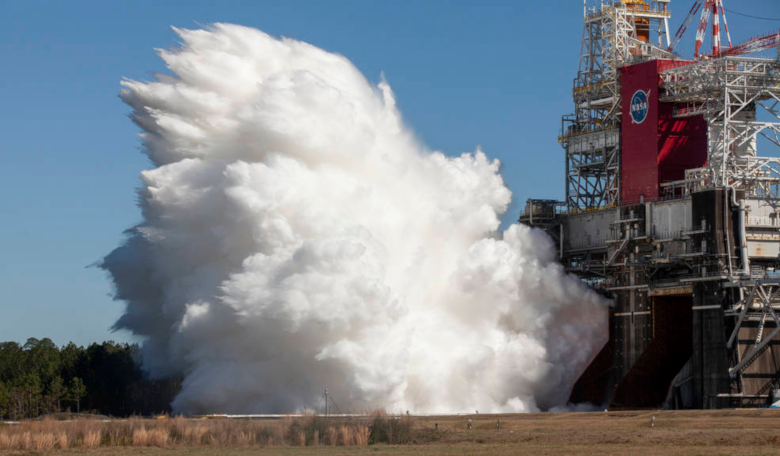
The largest rocket element NASA has ever built, the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, fired its four RS-25 engines for 8 minutes and 19 seconds Thursday at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The successful test, known as a hot fire, is a critical milestone ahead of the agency’s Artemis I mission, which will send an uncrewed Orion spacecraft on a test flight around the Moon and back to Earth, paving the way for future Artemis missions with astronauts.
Engineers designed the eight-part Green Run test campaign to gradually bring the SLS core stage to life for the first time, culminating with the hot fire. The team will use data from the tests to validate the core stage design for flight.
“The SLS is the most powerful rocket NASA has ever built, and during today’s test the core stage of the rocket generated more than 1.6 million pounds of thrust within seven seconds. The SLS is an incredible feat of engineering and the only rocket capable of powering America’s next-generation missions that will place the first woman and the next man on the Moon,” said acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk. “Today’s successful hot fire test of the core stage for the SLS is an important milestone in NASA’s goal to return humans to the lunar surface – and beyond.”
NASA previously conducted a hot fire test of the SLS core stage 16 January. The four RS-25 engines fired together for the first time for about one minute before the test ended earlier than planned. Following data analysis, NASA determined a second, longer hot fire test would provide valuable data to help verify the core stage design for flight, while posing minimal risk to the Artemis I core stage.
During the second hot fire test, the stage fired the engines for a little more than eight minutes, just like it will during every Artemis launch to the Moon. The longer duration hot fire tested a variety of operational conditions, including moving the four engines in specific patterns to direct thrust and powering the engines up to 109% power, throttling down and back up, as they will during flight.
“This longer hot fire test provided the wealth of data we needed to ensure the SLS core stage can power every SLS rocket successfully,” said John Honeycutt, manager for the SLS Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. “During this test, the team conducted new operations with the core stage for the first time, repeated some critical operations, and recorded test data that will help us verify the core stage is ready for the first and future SLS flights for NASA’s Artemis program.”
The two propellant tanks in the SLS core stage collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of supercold liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen to help fuel the RS-25 engines at the bottom of the stage. The core stage has a complex network of flight software and avionics systems designed to help fly, track, and steer the rocket during launch and flight. Prior tests in the Green Run test series evaluated the integrated functionality and performance of the core stage’s avionics systems, propulsion systems, and hydraulic systems.
“Today is a great day for NASA, Stennis and this nation’s human space exploration program. This final test in the Green Run series represents a major milestone for this nation’s return to the Moon and eventual mission to Mars,” said Stennis Center Director Richard Gilbrech. “So many people across the agency and the nation contributed to this SLS core stage, but special recognition is due to the blended team of test operators, engineers, and support personnel for an exemplary effort in conducting the test today.”
Test teams at Stennis supervised a network of 114 tanker trucks and six propellant barges that provided liquid propellant through the B-2 Test Stand to the core stage. Test teams also delivered operational electrical power, supplied more than 330,000 gallons of water per minute to the stand’s flame deflector, and monitored structural interfaces of both the hardware and the stand.
Testing the SLS rocket’s core stage is a combined effort for NASA and its industry partners. Boeing is the prime contractor for the core stage and Aerojet Rocketdyne is the prime contractor for the RS-25 engines.
Next, the core stage for SLS will be refurbished, then shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. There, the core stage will be assembled with the solid rocket boosters and other parts of the rocket and NASA’s Orion spacecraft on the mobile launcher inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy in preparation for Artemis I.
SLS, Orion, and the ground systems at Kennedy, along with the human landing system and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, are NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon on a single mission. The exploration of the Moon with NASA’s Artemis program includes preparations to send astronauts to Mars as part of America’s Moon to Mars exploration approach.