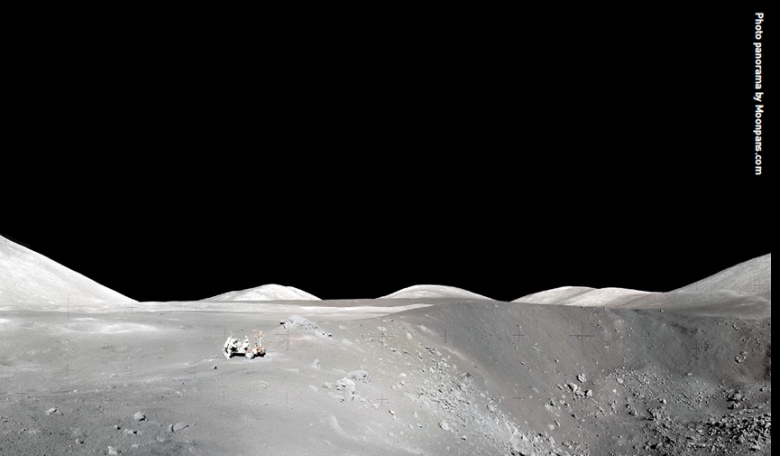
This year (2024) marked the start of a new era for space exploration. Increasingly, space missions are being led by commercial entities looking to exploit resources beyond near-Earth orbit and towards the Moon and Mars. Meanwhile, national governments across the world continue to explore outer space, as demonstrated by China’s lunar sample return mission in May 2024. This article links NewSpace and the Moon by introducing a concept that employs robotics and in-situ resource utilisation of the lunar regolith to construct plume deflection structures.
The ability to create large, strong structures on another planetary body without the need to transport all the materials lies at the heart of in-situ resource utilisation (ISRU) and represents a revolution for surviving on the Moon. A process that simultaneously removes lunar regolith from the local area and uses it to build structures will also improve working conditions by minimising the harmful effects of the abrasive dust on sensors and human support systems. The proposal described here will potentially enable the UK to develop a new capability, driven by scientific understanding, to support governments, science agencies and companies in surviving the extremely hostile environment on the Moon and, later, on Mars.
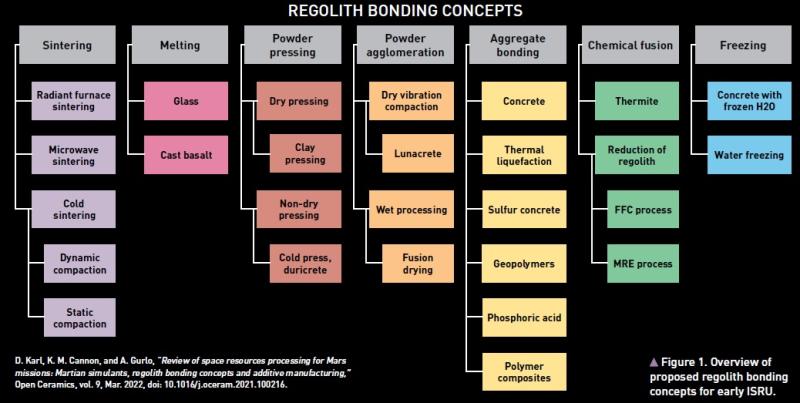
Regolith as a material
The lunar surface has two distinct elevation levels: the lowlands (dark patches known as maria or ‘seas’) and the highlands (lighter patches of mountainous areas). The lowland regions are understood to be dominated by lunar basalts, which are defined by a fine-grained matrix composed of roughly equal amounts of clinopyroxene and calcium-rich plagioclase. They frequently contain larger phenocrysts of forsteritic olivine, pyroxenes, plagioclase and iron-titanium oxides.
In the highland areas, lunar anorthosites dominate. They are characterised by a nearly mono-mineralic phase assemblage, consisting of over 90 percent calcic plagioclase and less than 10 percent magnesium-iron silicates (pyroxenes, olivine) and iron-titanium oxides (such as ilmenite and titanium spinel).
On the Moon, the predominant type of bedrock is ferroan anorthosite, a plutonic rock with a coarse crystalline texture and remote sensing data suggests regions with gabbroic (high calcium/aluminium) compositions. Additionally, mineral compositions in some Apollo 17 samples suggest these gabbroic lithologies are more prevalent in the lunar crust than their frequency in the Apollo sample collection would indicate.
What is clear from this is that the composition of the lunar regolith varies significantly from location to location. This makes developing any sort of standard construction material difficult as the constituent base materials differ across the surface.
The use of regolith as a building material can be categorised into two manufacturing processes. Historically, more focus has been placed on discrete building blocks (see Figure 1 on previous page), whereas recent advancements in continuous additive manufacturing techniques (for example, 3D printing demonstrations on the International Space Station) have shown that continuous methods are also possible. The advantage of discrete blocks is that they can be stronger, because they are often bonded under compression. Discrete manufacture may also allow the bricks to be produced in a location distant from where they are used. However, the discrete nature introduces inherent weaknesses in the interfaces between the blocks. The advantage of a continuous method is that such weak points are minimised and occur only between layers where the different lines of the extrusion meet.
To ensure that the ground beneath the construction site is stable, two primary techniques are available. The first - the Seismic Refraction and Reflection method - works by generating a seismic wavefront that travels away from the source and records the arrival of the wavefront at a receiver. The travel time of the wave is dependent on the velocity of the so-called P-wave in subsurface rock. Using geophones and seismometers as the receivers, the soil and rock properties, and thus the interfaces and faults can be determined. The second technology is Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR), which images the subsurface by generating an electromagnetic wave at the surface and recording it at the same position after reflection. This allows high resolution images to be obtained and assists in identification of voids, rock layers and other anomalies. It is also relatively cheap and fast.
Although there are many other methods, such as magnetic survey and electromagnetic induction survey, seismic refraction and reflection and GPR are the most reliable methods in cases where the properties of the subsurface rock are uncertain.
Hybrid concept
The ability to create large, strong structures on another planetary body without the need to transport all the materials lies at the heart of in-situ resource utilisation
Although the discrete and additive manufacturing methods each have their advantages, it is considered important to consider a hybrid approach - essentially, producing discrete building blocks and then using extrusion methods to ‘seal’ them together. It is, of course, important to consider which extrusion method is the most feasible from an energy and mass-efficiency standpoint, but the authors believe that priority should be given to mass efficiency as new developments in modular space reactors may allow high power production on planetary surfaces.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) categorises additive manufacturing techniques into seven groups:
- binder jetting
- direct energy deposition
- material extrusion
- material jetting
- powder bed fusion
- sheet lamination (not currently applicable for ISRU)
- vat polymerisation.
In order for such a hybrid approach to prove feasible, the manufacturing process must be integrated into a robotic system capable of laying bricks and extruding mortar. The robotic system can be a series of robotic machines each with different specialised functions (see Figure 2). Four major steps towards achieving this goal can be identified, as detailed in the following ‘roadmap’ for the future.
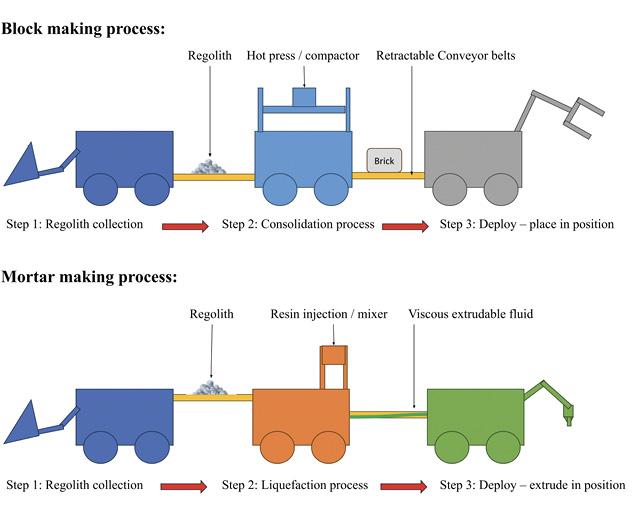 Figure 2. Illustrative concept of manufacturing/construction process.
Figure 2. Illustrative concept of manufacturing/construction process.
Step 1: identify a lunar soil simulant
The first step is to analyse data from past missions to the Moon and Mars to define the variations in regolith in terms of chemical and mineral structures. The performance of lunar soil simulants should be quantified; two key examples are known as TUBS-M and TUBS-T, named after the German university, TU Braunschweig, at which they were developed.
TUBS-M basalt is an alkali-olivine basalt found in Germany: it is fine-grained and dense and lacks degassing vesicles (see Figure 3). Other interstitial minerals include anorthoclase feldspar, iron oxides and zeolite, most likely formed from hydrous alteration of former basaltic glass. The bulk rock chemistry classifies TUBS-M as low titanium basalt and its alkali-rich nature is evident from elevated sodium oxide (Na2O) and potassium oxide (K2O) content compared to lunar samples.
 Figure 3. Thin section images of TUBS-M basalt (left) and TUBS-T anorthosite (right) under plane polarised and cross-polarised light (top and bottom images, respectively). Scale bar is 500 μm. Credit: S. Linke et al., TUBS-M and TUBS-T based modular Regolith Simulant System for the support of lunar ISRU activities, Planet Space Sci, vol. 180, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2019.104747.
Figure 3. Thin section images of TUBS-M basalt (left) and TUBS-T anorthosite (right) under plane polarised and cross-polarised light (top and bottom images, respectively). Scale bar is 500 μm. Credit: S. Linke et al., TUBS-M and TUBS-T based modular Regolith Simulant System for the support of lunar ISRU activities, Planet Space Sci, vol. 180, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2019.104747.
TUBS-M basalt has about 10 percent less iron oxide (FeO) than lunar basalts, highlighting the typical difference in total iron content between terrestrial and many lunar basalts. Terrestrial basalts generally range from five to 14 percent FeO, making it challenging to find an Earth basalt that matches the FeO content of lunar basalts. TUBS-M plagioclase is less aluminous and more silica-rich, resulting in lower calcium oxide (CaO) concentration compared to lunar plagioclase. A higher Na2O content by three percent reflects the alkali-enriched nature of TUBS-M basalt.
Although the discrete and additive manufacturing methods each have their advantages, it is considered important to consider a hybrid approach
TUBS-T generally matches the average chemical composition of lunar anorthosites, with only moderate enrichment of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Notably, the Na2O content is ten times higher than the lunar average due to the Moon’s characteristic Na-depletion. The loss on ignition (LOI), indicating the total volatile content in the rock, is about 1 percent, which is higher than expected for lunar anorthosites, as no liquid water is present on the Moon to form hydrous minerals, but it is typical for terrestrial equivalents due to the presence of water causing the crystallisation of hydrous minerals.
To identify a suitable anorthosite source representative of the lunar equivalent, various anorthosite deposits worldwide were examined, resulting in the selection of a Scandinavian anorthosite as the source material. The TUBS-T anorthosite is part of a Scandinavian metamorphosed gabbroic complex. Analysis of a thin section shows that the primordial magmatic texture appears altered by tectonic and metamorphic events: plagioclase crystals show recrystallisation due to tectonic stress (Figure 3), with some larger clasts remaining in the finer feldspar matrix.
It is worth mentioning that while the regolith can be used as a substitute for sand in cement, the lime portion of cement is almost impossible to replace. Finding lime (calcium oxide, CaO) directly on the Moon is unlikely, as lime is typically produced by heating calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to high temperatures. Naser’s 2018 review of extraterrestrial construction materials proposes chemical processes which could create CaO as well as other necessary base materials.
Transporting from Earth involves significant logistical challenges due to the constraints of space travel, particularly payload weight and volume limitations. Today’s launch vehicles have strict payload limits. For example, the Space Launch System (SLS) and SpaceX Starship, two of the largest proposed heavy-lift rockets, can carry payloads up to hundreds of tons to the Moon.
The exact amount of lime that can be transported depends on the specific mission and available payload capacity after accounting for essential supplies, equipment and crew. Lime is relatively dense, with a density of approximately 3.3 g/cm3 (3,300 kg/m3) and one ton of lime would occupy about 0.3 cubic metres. Given the high payload capacity of modern rockets, theoretically, 10 tons of lime could be transported. Lime content ranges from five to 15 percent, meaning that up to 100 tons of concrete could be manufactured on the Moon using lime from one launch.
Transporting materials to the Moon is extremely expensive, with costs currently estimated at around US $1 million to $2 million per kilogram. That would be $20 million alone for the lime, while ignoring the cost of any structural storage vessel. Given the high cost and limited volume, it could be more practical to produce lime on the Moon using lunar materials (e.g., extracting calcium from anorthite and processing it into lime) rather than transporting large quantities from Earth.
Calcium is present on the Moon, mainly in the form of calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar (anorthite, CaAl2Si2O8) and the lunar regolith contains significant amounts of plagioclase, which includes calcium. Through appropriate processing, calcium could be extracted and then converted to lime. Lunar maria are primarily composed of basaltic rocks containing minerals such as pyroxene and olivine, which include calcium as one of their components.
So, in summary, while lime in its pure form has not been found on the Moon, the raw materials necessary to produce lime are present. If future lunar missions had high energy power sources, it would be possible to develop the technology to process these materials to produce lime for use in various applications such as construction and habitat building.
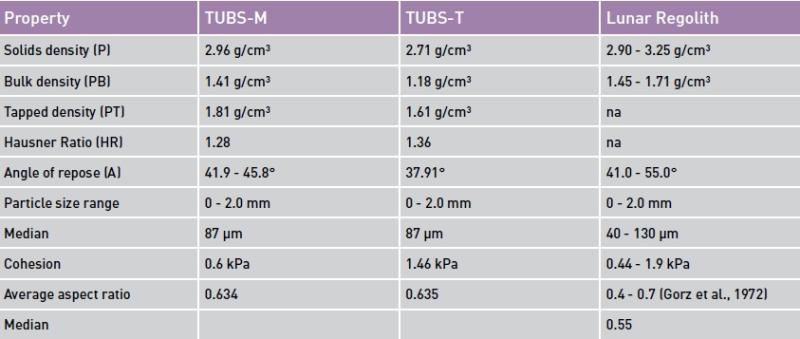 Figure 4 - Some physical properties of TUBS-M and TUBS-T compared to real lunar regolith. Credit: S. Linke et al., TUBS-M and TUBS-T based modular Regolith Simulant System for the support of lunar ISRU activities, Planet Space Sci, vol. 180, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2019.104747.
Figure 4 - Some physical properties of TUBS-M and TUBS-T compared to real lunar regolith. Credit: S. Linke et al., TUBS-M and TUBS-T based modular Regolith Simulant System for the support of lunar ISRU activities, Planet Space Sci, vol. 180, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2019.104747.
Step 2: develop and test a bonding process
The proposed process would convert regolith into an extrudable material which, when solidified, meets thermal and mechanical requirements
The proposed process would convert regolith into an extrudable material which, when solidified, meets thermal and mechanical requirements. The selected brick and mortar method must be tested with a variety of regolith materials to quantify the performance of the final material with respect to changes in chemical composition.
An initial set of guidelines should be developed and shared for other researchers looking to do similar work. For example, if the mortar produced is of poor quality due to certain chemical compositions, repointing could be performed to repair the cracks after a first application (in a similar manner to Earth-based construction). Repointing is a crucial masonry maintenance process that involves removing and replacing deteriorated mortar between bricks (see Figure 5).
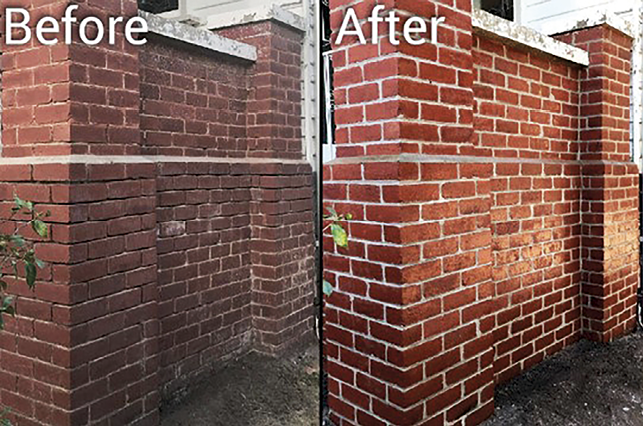 Figure 5. A wall before repointing and after repointing.
Figure 5. A wall before repointing and after repointing.
Step 3: integrate the process into a rover
Once the process has been developed, it must be integrated with a lunar rover to provide a mobile printing capability to enable the additive manufacturing of solid structures. A key part of the success of lunar manufacturing will be the development of ‘swarms’ of rovers capable of building the required structures.
A proof-of-concept could be demonstrated in collaboration with the STFC Boulby Underground Laboratory, which is situated 1.1 kilometres below the UK’s North Yorkshire Moors (see Figure 6). The science conducted at Boulby now is highly multidisciplinary and hosts a wide range of scientific studies that require experimental space or access to the geologically interesting deep underground environment. The Boulby Laboratory’s unique environment allows for rigorous testing of these systems under conditions that simulate the harsh realities of space, ensuring their reliability and effectiveness in extraterrestrial applications.
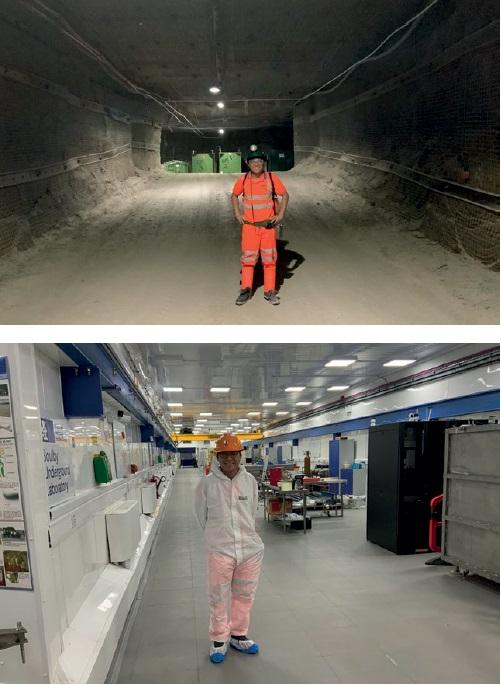 Figure 6. Images inside STFC Mine and inside the underground laboratory.
Figure 6. Images inside STFC Mine and inside the underground laboratory.
Step 4: simulate and validate plume-structure interaction
Once a construction method has been proven, simulations of how rocket plumes interact with physical structures should be carried out to understand how these structures should be designed to deflect these plumes.
For example, the University of Glasgow’s Plume Regolith Facility is one of the seven official European Space Agency (ESA) designated strategic facilities distributed across Europe and is the only one that enables the realistic simulation of planetary conditions and testing of plume-regolith problems and interactions (see Figure 7). The facility is aligned with ESA’s robotic exploration programme requirements for missions including Mars Sample Return.
A critical aspect of its work involves the simulation and validation of plume-structure interactions using advanced computational tools
A critical aspect of its work involves the simulation and validation of plume-structure interactions using advanced computational tools such as OpenFOAM. This open-source software enables researchers to model the complex behaviour of regolith particles when disturbed by rocket plumes during landing and takeoff. By accurately simulating these interactions, the facility aims to understand and mitigate the potentially harmful effects of dust and debris on spacecraft and surface structures, insights crucial for designing landing systems and constructing stable habitats on other planets.
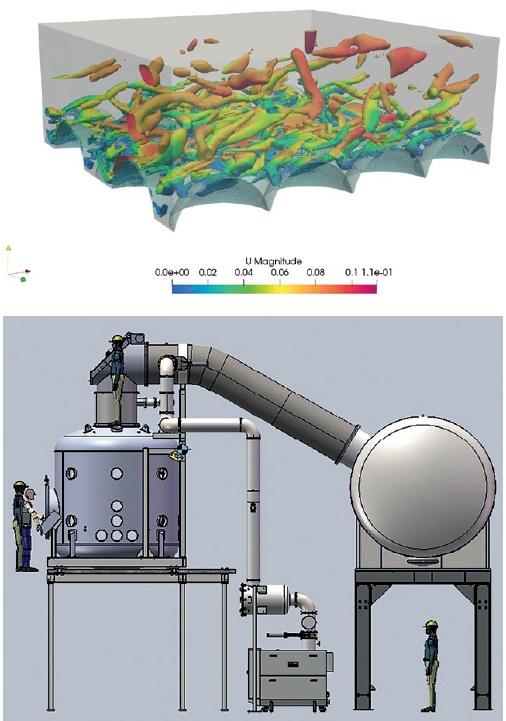 Figure 7. Top: Examples of OpenFOAM and OpenSeesPy Simulation; above: CAD model of dirty vacuum chamber facility.
Figure 7. Top: Examples of OpenFOAM and OpenSeesPy Simulation; above: CAD model of dirty vacuum chamber facility.
Future roadmap
Driven by a deep scientific understanding of the regolith and in-situ resource utilisation, the proposed roadmap will lead to the creation of a specific data exploitation plan for Lunar and Martian robotic exploration. The future works proposed will directly increase the technology readiness levels of the systems needed for extraterrestrial construction.
Meanwhile, researchers studying regolith for construction (such as the Osaka Institute of Technology and Korea Aerospace Research Institute) and instrument developers (such as University College London’s Mullard Space Science Laboratory) will be able to improve the correlation between spectral imaging of regolith and the actual chemical composition.
Editor’s note
Readers interested in collaborating on this work for the Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre (AMRC - www.amrc.co.uk) at the High Value Manufacturing Catapult (HVMC) are welcome to contact the authors for further discussion.
About the authors
Dr Yun-Hang Cho is an Engineer with over 10 years of project experience and more than 10 academic publications (including planetary science with Caltech). He currently leads Space Sector Engagement at the University of Sheffield’s Advanced Manufacturing Research Centre. Dr Cho has led several balloon science programmes to deliver scientific payloads for European and US launches, and his previous work includes nuclear-hydrogen co-generation funded by the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy, as well as EU Horizon 2020 (HEMERA) programmes. He is also a member of the Space Academic Network (SPAN) and signatory to the SciSat proposal.
Xinhui Shen is a second-year Earth and Planetary Science student at Imperial College London and an active member of the science team at the Imperial Planetary Robotics Lab (IPRL). She has participated in six field trips, acquiring extensive field skills. Shen also led a team in writing an essay using LaTeX, titled Dynamic Behavior for an SIRS Model with Nonlinear Incidence Rate and Treatment, which was published in Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).














