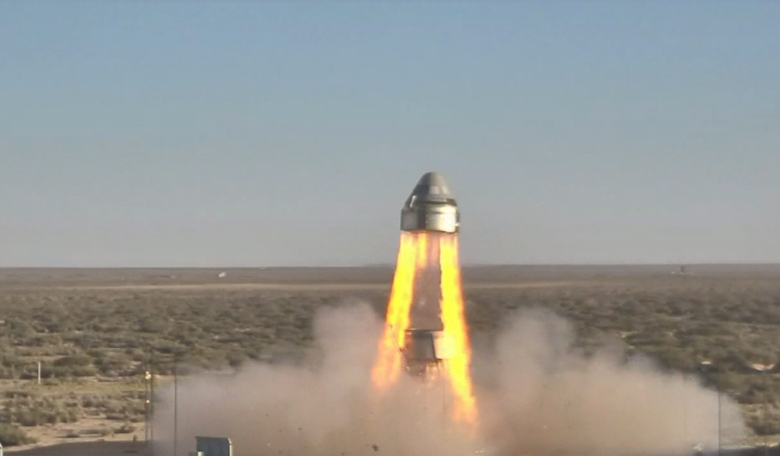
Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft completed a critical safety milestone on Monday in an end-to-end test of its abort system. The Pad Abort Test took place at Launch Complex 32 at the U.S. Army’s White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico.
The test was designed to verify each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This was Boeing’s first flight test with Starliner as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight launches to the International Space Station from American soil.
“Tests like this one are crucial to help us make sure the systems are as safe as possible,” said Kathy Lueders, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program manager. “We are thrilled with the preliminary results, and now we have the job of really digging into the data and analyzing whether everything worked as we expected.”
During the test, Starliner’s four launch abort engines, and several orbital maneuvering and attitude control thrusters simultaneously ignited to rapidly push the spacecraft away from the test stand. Five seconds into flight, the abort engines shut off as planned, transferring steering to the control thrusters for the next five seconds.
A pitcharound maneuver rotated the spacecraft into position for landing as it neared its peak altitude of approximately 4,500 feet. Two of three Starliner’s main parachutes deployed just under half a minute into the test, and the service module separated from the crew module a few seconds later. Although designed with three parachutes, two opening successfully is acceptable for the test perimeters and crew safety. After one minute, the heat shield was released and airbags inflated, and the Starliner eased to the ground beneath its parachutes.
The demonstration took only about 95 seconds from the moment the simulated abort was initiated until the Starliner crew module touched down on the desert ground.
“Emergency scenario testing is very complex, and today our team validated that the spacecraft will keep our crew safe in the unlikely event of an abort,” said John Mulholland, Vice President and Program Manager, Boeing’s Commercial Crew Program. “Our teams across the program have made remarkable progress to get us to this point, and we are fully focused on the next challenge—Starliner’s uncrewed flight to demonstrate Boeing’s capability to safely fly crew to and from the space station.”
Boeing’s next mission, called Orbital Flight Test, will launch an uncrewed Starliner spacecraft to the station on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. Launch is targeted for Dec. 17.