 02 October 2018
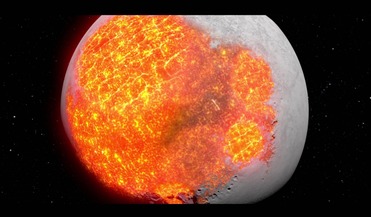
New technique could provide fresh insights into how the Moon was formed
02 October 2018
New technique could provide fresh insights into how the Moon was formed
... that is formed from the rapid cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich lava; basalt. More than 90 percent of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt and around 16 percent of the lunar surface – the dark patches known as Mares...
 10 December 2018
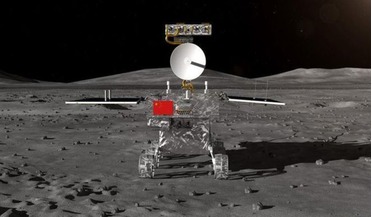
First far side of the Moon mission underway
10 December 2018
First far side of the Moon mission underway
...side that is dominated by huge lunar mares – large, dark basaltic plains, that were initially mistaken for seas by early lunar observers.... magmas to erupt on the surface, limiting the amount basalts available to create the maria. Why is the farside ...
 January 2018
When it comes to water Mars may not be the promised land
January 2018
When it comes to water Mars may not be the promised land
... example of lava filled craters. Indeed, the majority of the impact craters on Mars are filled by lava and/or by basaltic sands of volcanic origin transported by the wind. The solar arrays on NASA’s InSight lander are deployed in this...
 February 2018
European centre shifts emphasis to deep space missions
February 2018
European centre shifts emphasis to deep space missions
.... The testbed will comprise a lunar regolith simulant sourced from the local Eifel region volcanic and basalt sources, which provides a satisfactory mechanical and compositional simulant. The simulant testbed area is planned to be 50 cm in depth...
 November 2020
Walking on the Moon
November 2020
Walking on the Moon
... lava tubes, which a traditional wheeled rover might find challenging. Lava tubes are subsurface tunnels, formed by basaltic lava flows – on Earth and on the Moon - and have long been proposed as viable locations for future...
 23 June 2016
Newly found mineral on Mars hints at explosive volcanism
23 June 2016
Newly found mineral on Mars hints at explosive volcanism
... associated with silicic volcanism, an explosive type of volcanism that on Earth can cover vast areas called flood basalt provinces, but on Mars, tridymite was not thought to be important or even present. Accordingly, this discovery throws into...