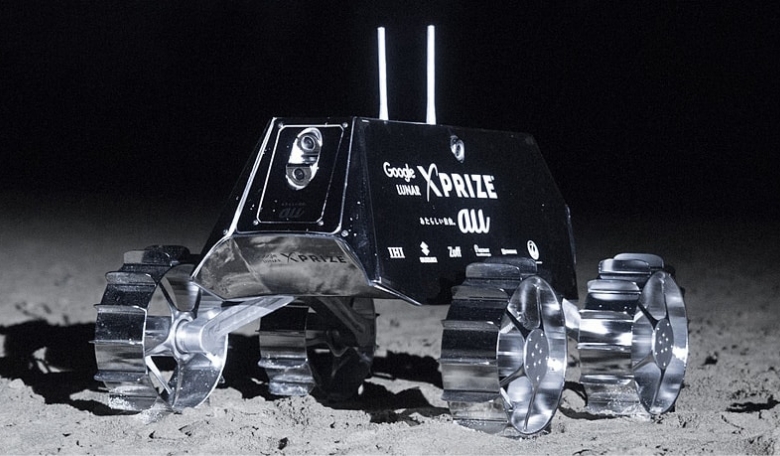
It has been said many times before that to become a multi-planet species, we must first be able to conquer the Moon and use its resources effectively before making the leap to other worlds. To achieve this aim, a team based in the Space Robotics Lab at Tohoku, Japan, are working on a high-speed, improved-mobility rover to help identify regions of interest on the lunar surface. Could this be the start of a journey that will eventually help humans get to Mars in the 2030s?
With many of the present and future space exploration missions revolving around the exploitation of the Moon, there is a need to gather the knowledge and to develop the technology that will eventually make these missions affordable and sustainable. Unlike life in low Earth orbit (LEO) where resources can be brought form the ground, for humans to thrive beyond LEO resources have to be found, extracted, processed, managed and used directly at the place of exploration. Characterising the local environment in the search for specific resources is the first necessary step of the voyage that humankind is already undertaking to explore and inhabit the Solar System.
In this endeavour, robots are set to play a key role by working side-by-side with humans and the objective of our mission at the Space Robotics Lab at Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, is to develop the capabilities for planetary robots to be more efficient in reaching positional targets, more effective in the selection of regions of interest, and more reliable in overcoming the obstacles and withstanding the risks of performing in outer space. Our plan to develop a high-speed, improved-mobility rover is just the beginning of a journey that will take humans farther into the Solar System than ever before.
Read more about lunar rovers developed by Space Robotics Lab in the full version of the article, available now to our subscribers.