 03 April 2018
Astronomers unexpectedly find the most distant star ever discovered
03 April 2018
Astronomers unexpectedly find the most distant star ever discovered
... new insights into the constituents of the galaxy cluster. We know that the microlensing was caused by either a star, a neutron star, or a stellar-mass black hole,” explains Steven Rodney from the University of South Carolina, USA and a co-author...
 11 January 2021
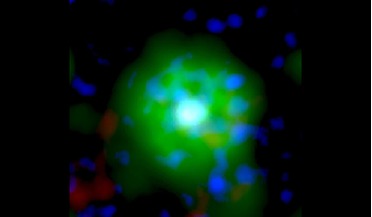
Strange star unlike any seen before, scientists say
11 January 2021
Strange star unlike any seen before, scientists say
... and will likely collapse into another type of small dense star known as a neutron star within 10, 000 years. “Its fate will therefore be to undergo core collapse and to form a neutron star,” write the authors in their recent research paper. “Over...
 27 February 2017
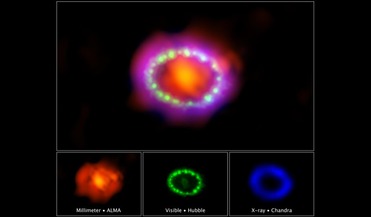
Thirty years in the making - researchers show SN1987A in all of its glory
27 February 2017
Thirty years in the making - researchers show SN1987A in all of its glory
... any evidence for either of these objects yet. To see SN 1987A in all of its glory (minus a black hole or neutron star), the latest visuals can be seen here, here and here (all links open up in a new window). These...
 06 May 2020
Astronomers find closest black hole to Earth
06 May 2020
Astronomers find closest black hole to Earth
... a similar configuration to HR 6819 or LB-1, but where the inner pair is made up of two black holes or of a black hole and a neutron star. The distant outer object can gravitationally impact the inner pair in such a way that it triggers a merger...
 February 2017
Global robotic network for monitoring near-Earth and outer space
February 2017
Global robotic network for monitoring near-Earth and outer space
... of the accelerated expansion of the Universe. The appearance of next-generation gravitational wave interferometers has made researching neutron star mergers and black holes possible, whereas medium and large diameter telescopes can find the furthest...
 27 October 2021
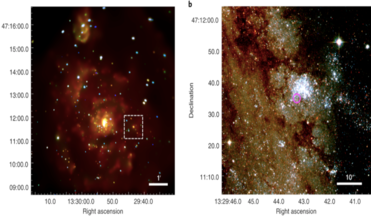
Astronomers may have detected the first planet outside of the Milky Way
27 October 2021
Astronomers may have detected the first planet outside of the Milky Way
... from x-ray bright binaries. These luminous systems typically contain a neutron star or black hole pulling in gas from a closely orbiting companion star. The material near the neutron star or black hole becomes superheated and shoots off x-rays...