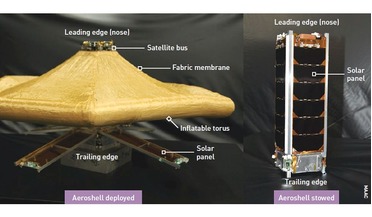
 February 2020
Aeroshells – from LEO to Mars
February 2020
Aeroshells – from LEO to Mars
...deployment mechanism. Debris mitigation LEO is one of the most commercially valuable regions of outer space (second only to geostationary orbit, GEO), and is situated between altitudes of about 150 km and 2000 km. The key letter in the acronym is the...
 November 2025
Extra-terrestrial Skyring: managing space debris with an artificial planetary ring
November 2025
Extra-terrestrial Skyring: managing space debris with an artificial planetary ring
... ‘resonance gaps’, which would provide a form of safe parking orbit where space debris can be transported. The one we are all familiar with is geostationary orbit (GEO), a 1:1 resonance at an altitude of 35,786 km, but this is widely used for active...
 September 2025
AI cybersecurity - challenges in space
September 2025
AI cybersecurity - challenges in space
... and complexity, and residual risks always remain. Communication with space assets, particularly those in geostationary orbit (GEO) or deep space, is subject to significant signal propagation delays (latency) and constrained data transmission rates...
 01 June 2021
Space junk collision highlights need for intervention
01 June 2021
Space junk collision highlights need for intervention
...larger than 5-10 cm in low Earth orbit (LEO) and 30 cm to 1 m in geostationary orbit (GEO) - as well as several thousands to millions of non-trackable debris particles in orbit around the Earth. “These in-orbit collisions and explosions highlight the...
 May 2019
Active debris removal faces legal minefield
May 2019
Active debris removal faces legal minefield
...measures to remove objects from low Earth orbit (LEO) and geostationary orbit (GEO) after the end of their missions... could apply to tacit consent in the context of these in-orbit operations. ESA is planning the world’s first ever active debris...
 August 2020
Battle for the night sky - from telescopes to ad-breaks
August 2020
Battle for the night sky - from telescopes to ad-breaks
... from space. Previous attempts to provide this service focused on larger, more powerful and more expensive satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO), but they faced the issue of longer signal delays because of the greater distance compared with LEO...