 01 June 2021
Space junk collision highlights need for intervention
01 June 2021
Space junk collision highlights need for intervention
... services. It is estimated that there are around 34,000 trackable objects - larger than 5-10 cm in low Earth orbit (LEO) and 30 cm to 1 m in geostationary orbit (GEO) - as well as several thousands to millions of non-trackable debris particles...
 March 2015
Sky links: from multi-satellite systems to nano-launchers
March 2015
Sky links: from multi-satellite systems to nano-launchers
... that is still widely used. The effective use of the spectrum by large SC during television transmission from geostationary orbit is telling – the same frequency may be used by satellites in different positions and additionally radiate with different...
 March 2016
Saving Earth from an Expanding Sun
March 2016
Saving Earth from an Expanding Sun
...asteroid at the L1 or L2 or L5 Lagrangian points of Earth’s orbit and tug Earth away. Sound implausible? Maybe it’s time to take ... a very, very long tether from Earth to above geostationary orbit, secured to a counterweight, it could be possible to...
 August 2017
On-orbit assembly will deliver major benefits in coming decade
August 2017
On-orbit assembly will deliver major benefits in coming decade
... and provide launch savings of several hundred million dollars. Communications satellites On-orbit assembly can also provide payoff for telecommunications in geostationary orbit (GEO). Consider the data distribution sector where the satellite is used...
 January 2019
Preparing for a robotic revolution in Earth orbit
January 2019
Preparing for a robotic revolution in Earth orbit
...; it produces no greenhouse gases, radioactive waste, pollution, or scarring of the Earth for resources; and from geostationary orbit, it is most efficiently received at low latitudes, where much of the Earth’s population growth is occurring. Japan...
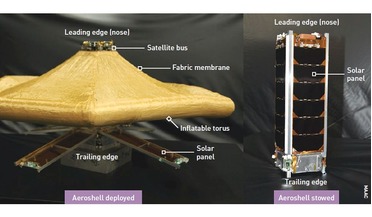 February 2020
Aeroshells – from LEO to Mars
February 2020
Aeroshells – from LEO to Mars
...deployment mechanism. Debris mitigation LEO is one of the most commercially valuable regions of outer space (second only to geostationary orbit, GEO), and is situated between altitudes of about 150 km and 2000 km. The key letter in the acronym is the...