 20 November 2019
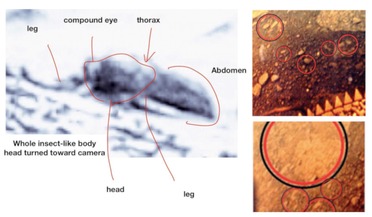
Insects on Mars, fungi on Venus. Evidence is presented for life on our neighbouring planets
20 November 2019
Insects on Mars, fungi on Venus. Evidence is presented for life on our neighbouring planets
...hold in the ~4.5 billion years since the birth of the Solar System? Not necessarily so, say two scientists working on two ...upper atmosphere and blown to Mars and Venus via powerful solar winds, through microbes hitching a ride on space crafts, or...
 15 June 2020
Green dayglow detected at Mars for the first time
15 June 2020
Green dayglow detected at Mars for the first time
... auroras and they are caused by the interaction of the solar wind (charged particles flowing from the Sun) with a planet’s... like auroras. They are also generated by the interaction of solar radiation with molecules in the upper atmosphere – not with a...
 July 2016
France, Europe and Russia - two decades of space launch cooperation
July 2016
France, Europe and Russia - two decades of space launch cooperation
... the European Space Agency (ESA). The initial mission, which was dedicated to the study of interactions between solar winds and terrestrial magnetosphere, was soon followed by two additional Cluster II satellites on 9 August. Three years later...
 December 2017
Panoramas from the surface of the Moon
December 2017
Panoramas from the surface of the Moon
... picking up the Lunar Surface Drill. The white box-type object at the bottom of the shot is the Solar Wind Spectrometer and to the right of that is the Heat Flow Electronics box. Mount Hadley and the Swann...
 21 July 2015
“EPIC” Earth from NASA and DSCOVR: Stunning image taken from a million miles away
21 July 2015
“EPIC” Earth from NASA and DSCOVR: Stunning image taken from a million miles away
... allowing scientists to study daily variations from the entire planet. DSCOVR’s main mission is to maintain real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities, in order to produce more accurate and timely space weather alerts from NOAA. What’s particularly...
 30 December 2019
Will Betelgeuse go supernova soon? Probably not say some astronomers
30 December 2019
Will Betelgeuse go supernova soon? Probably not say some astronomers
... dust that follows the explosion typically travels at around 10,000 kilometres per second (for comparison, the solar wind reaches around 450 kilometres/sec). This means it wouldn’t arrive at our planet until about 100,000...