 April 2024
The promise of solar energy for sustainable development and space exploration
April 2024
The promise of solar energy for sustainable development and space exploration
... locations. Space-based solar power involves transforming solar power into electricity via photovoltaic cells in geostationary orbit around Earth. The power is then transmitted wirelessly in the form of microwaves at 2.45 GHz to dedicated receiver...
 12 March 2018
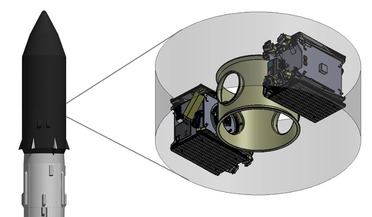
Satellite-servicing space drones set for launch in 2020
12 March 2018
Satellite-servicing space drones set for launch in 2020
...deep space exploration and space manufacturing logistics. “Launching our first two SPACE DRONE™ spacecraft into a geostationary orbit is part of our strong commitment to our first customer, meeting mission timeline and ensuring smooth transition into...
 18 October 2019
Companies unite to reject SpaceX satellite plans
18 October 2019
Companies unite to reject SpaceX satellite plans
... Commission defer consideration of SpaceX’s intention to modify its license for a Ku/Ka-band non-geostationary orbit as “SES entities operate both NGSO and geostationary orbit (“GSO”) FSS networks that use these bands.” Not only is that a problem say...
 March 2015
On-orbit satellite servicing, insurance and lessons of Palapa B2 and Westar 6
March 2015
On-orbit satellite servicing, insurance and lessons of Palapa B2 and Westar 6
... all insurers and satellite owners, with more than 200 dead satellites in geostationary orbit. Of even greater concern for operators with assets in lower Earth orbits is the additional threat of collision from thousands of launch vehicle spent parts...
 October 2015
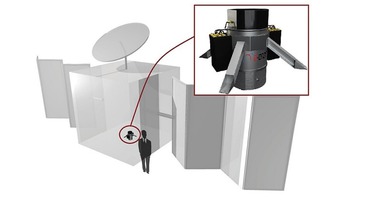
Down to Earth: how to deorbit satellites and save money
October 2015
Down to Earth: how to deorbit satellites and save money
... that prevents it being controlled from the ground. This has great value in different situations. In the case of geostationary orbit, where narrow slots are assigned to operators, a satellite has to be removed in order to make way for the newer...
 March 2019
Urgent action needed to avert space debris threat
March 2019
Urgent action needed to avert space debris threat
... impossible. This could be the case not only for LEO, but also for medium Earth orbit (MEO) and geostationary orbit (GEO). So, it is absolutely imperative that we tackle the issue of congestion and debris in space before LEO constellations...